The gap between what users search for and what they actually find results in a loss of genuine user engagement.
Climatebase, a climate jobs platform, experienced this firsthand with Algolia before migrating to Superlinked. Although Algolia’s feed served over three times more job search queries, Superlinked achieved double the bookmarking rate per query. This indicates that users find Superlinked's matches to be much more relevant and engaging.
Search systems like Algolia use exact keyword matching, which limits their ability to understand user intent. These systems rely on rigid filters and fixed attribute indexing, which fragments context and diminishes the relevance of search results. Consequently, this leads to frustrating user experiences.
Superlinked addresses this challenge by using vector embeddings to understand meaning across text, images, and metadata. It integrates different data modalities into a unified vector query layer, enabling more context-aware search.
If you are currently using Algolia and planning to migrate to Superlinked, this guide provides helpful tips to ease your transition.
Both Algolia and Superlinked are search solutions, but they operate very differently.
Algolia is a hosted search-as-a-service (SaaS) platform, providing a complete suite of tools for building search and discovery experiences.
Superlinked is a full-stack AI search platform that lets teams deploy a complete search environment with indexing logic, querying, and scalable infrastructure.
With increasing data volumes, Algolia’s pricing model, which is based on the number of operations and index record size limit, can become costly. This limitation requires splitting long documents into smaller chunks. Superlinked, on the other hand, reduces search costs and provides fine-grained control over data, infra, embeddings, and search logic to build highly customized and advanced search systems.
While Algolia has introduced new features, its core architecture is still anchored in keyword matching. Multimodel search (blending text, images, and diverse metadata) and dynamic profile filtering remain limited or require complex workarounds due to the rigid SaaS structure. Traditional keyword-and-filter search systems like Algolia look for exact matches of the words and phrases that are entered. They struggle with synonyms and ambiguous phrasing because they match literal terms rather than the underlying meaning.
While Algolia uses a suite of AI algorithms for search and re-ranking, no single AI algorithm can simultaneously address these challenges in production. Superlinked uses vector embeddings to comprehend meaning beyond literal terms. It represents the next generation of AI search for enterprises needing unified multimodal search across text, images, and metadata.
Here’s an example of how Climatebase transitioned from Algolia to Superlinked to achieve better results.
Climatebase is a leading hiring platform for climate careers, serving over 1 million people annually. It required a search and recommendation system capable of quickly and effectively connecting diverse talent with impactful climate jobs.
The previous search-based system, powered by Algolia, relied primarily on keyword-based search results and static ranking logic. Many job seekers received results that did not align with their backgrounds, domain interests, or preferred work styles. The platform experienced a low view-to-application rate of approximately 1%. User feedback highlighted issues with relevance and mismatched listings, resulting in a 0.7% job dislike rate.
Superlinked was integrated as an AI-powered recommendation platform to enhance personalized job feeds.
It encodes rich information about job posts and user profiles into high-dimensional vectors.
It combined specialized language and skill encoders with metadata-aware embeddings using a mixture-of-encoders architecture.
It adapts recommendations based on real-time user behavior as candidates browse, save, or apply.
It scales and manages the infrastructure of vector ingestion
Users engaged more with surfaced listings and saved jobs with more confidence. Application efficiency improved significantly, driven by more accurate role alignment and relevance matching.
Users applied for jobs 50% more often, increasing the view-to-application rate from 1.04% with Algolia to 1.57%.
The bookmarking rate per query was twice that of Algolia.
Satisfaction with job types increased by 50%, reducing role-mismatch complaints by approximately half.
 How Superlinked unifies your ingestion and querying logic
How Superlinked unifies your ingestion and querying logic
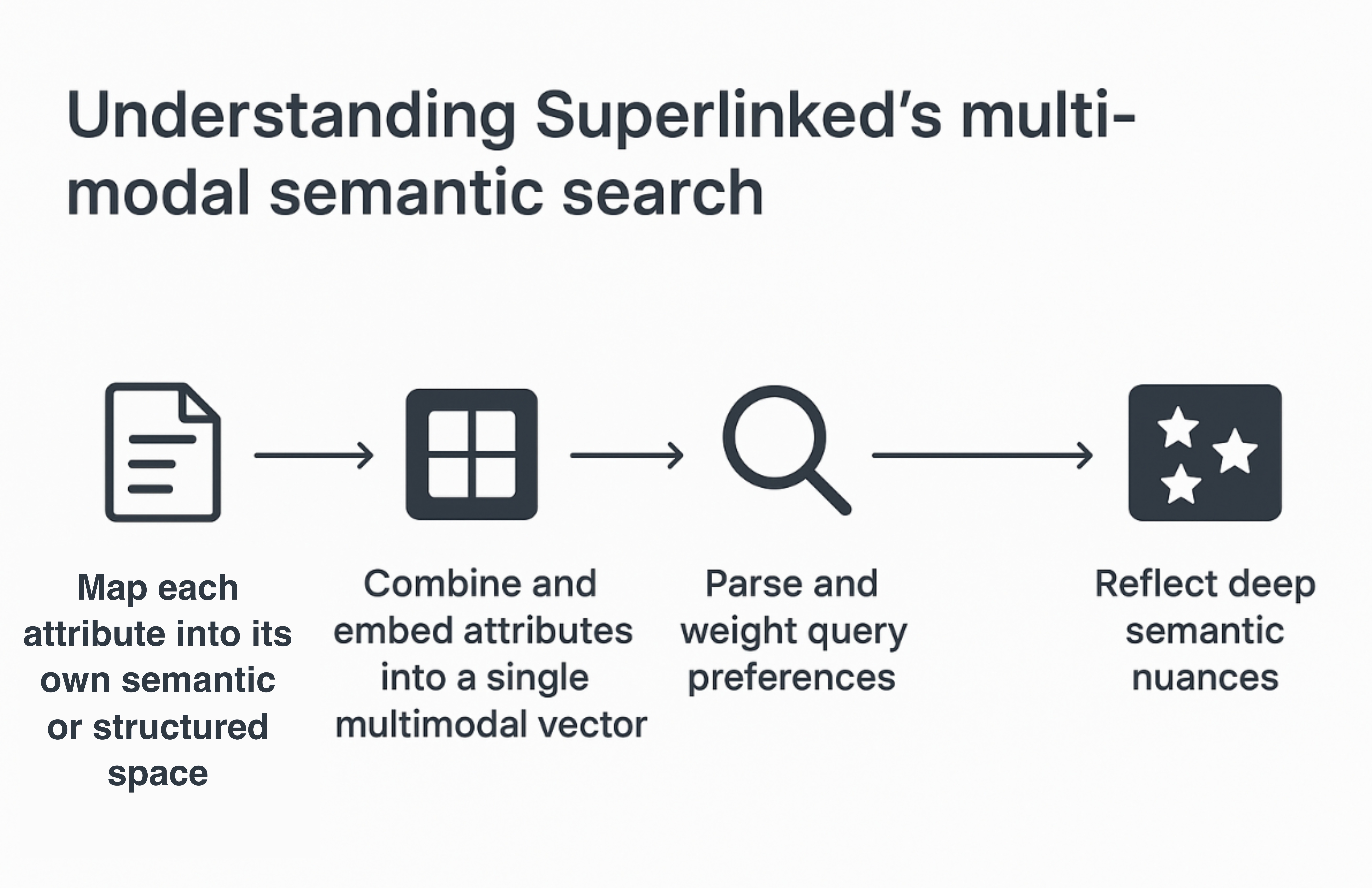
Superlinked derives meaning from data rather than just words by encoding each attribute of an entity with its own specialized model. Text, images, numeric values, and categorical fields are each embedded or encoded separately using the appropriate modality-specific encoder. These representations are then fused into a unified multimodal vector that captures both semantic and structured signals for the entity.
This multimodal embedding enables efficient similarity-based retrieval across diverse data types. Superlinked performs its core work at query time, where your querying code transforms a user’s natural-language input into weighted vector operations. Each attribute or modality can receive different weights to surface the most relevant results.
Users can adjust attribute weights at query time without re-indexing, and a natural-language interface can map plain-language queries into these weighted preferences automatically. For example, a user might emphasize semantic meaning from a description over numeric popularity, or the reverse. These adjustments happen dynamically and do not require recomputing the underlying embeddings.
So, results always reflect the deep semantic nuances that are present throughout the entire search process.
Check out this vector database comparison table to explore the trade-offs among different vector databases and make an informed decision for your Superlinked setup.
To plan your migration effectively, it's essential to understand the fundamental differences in how Superlinked and Algolia process and store data.
 From prefix search to full stack AI
From prefix search to full stack AI
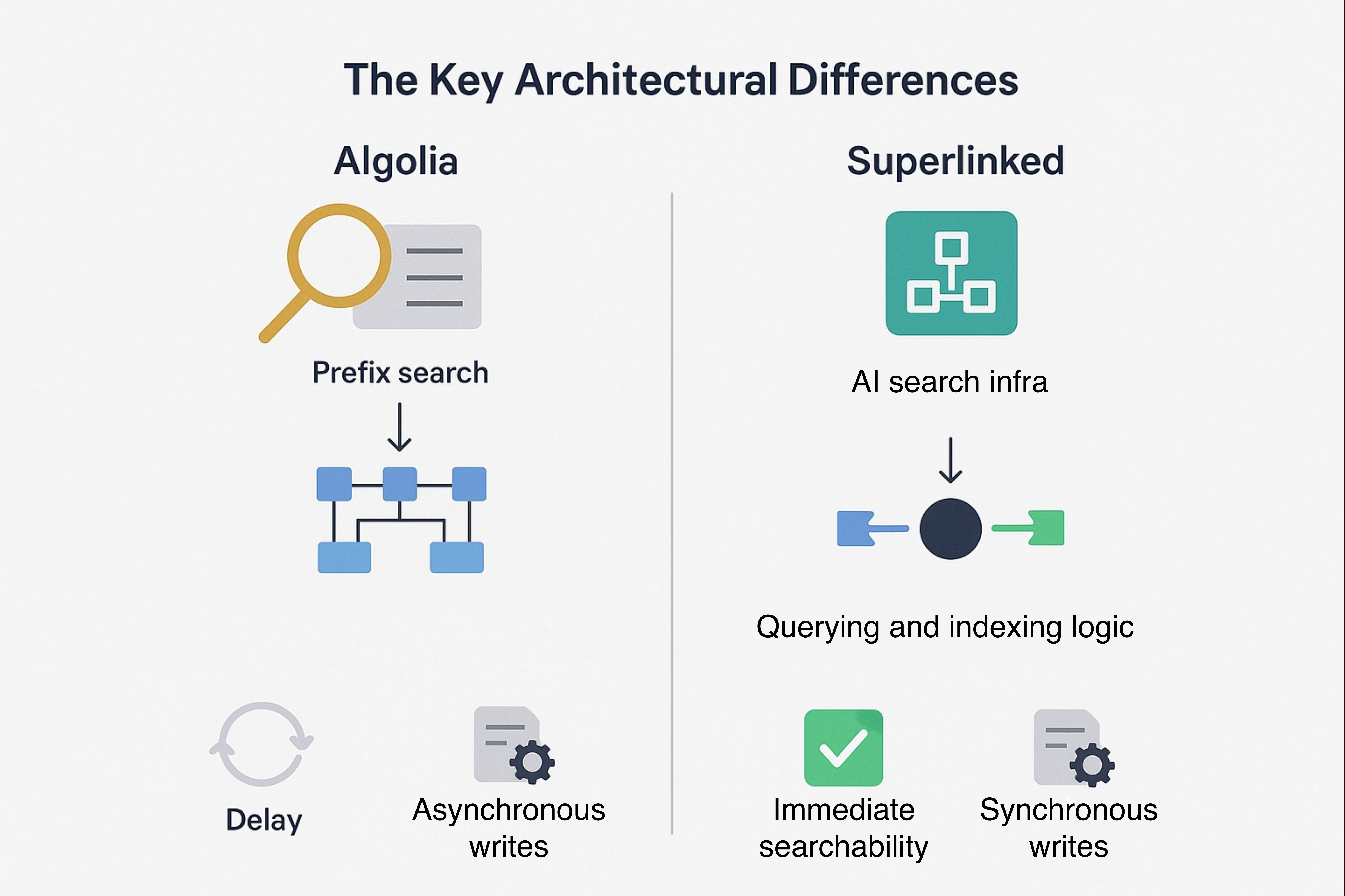
By default, Algolia uses prefix search, which matches query terms at the beginning of words in your records. This method is optimized for token-level speed, but its standard prefix-based search does not support semantic understanding across fields.
Superlinked introduces an AI-native search infrastructure layer that lets teams own their search logic while we handle the hard production problems. These problems are usually around vector indexing and ingestion pipeline as well as querying logic. As a platform it is explicitly built for production, iteration, and scale, not just a “vector add-on”.
In Algolia, all write operations, such as adding or updating records, are asynchronous. Each operation is queued, and data becomes searchable only after the task is processed. This can introduce a short delay before updates appear in search results.
Superlinked’s in-memory and persistent executors perform synchronous writes. When you add a record, it is processed immediately and becomes searchable right away.
This enables fast iteration and a reliable development feedback loop.
Migrating from Algolia to Superlinked means moving from a hosted search engine to a fully controllable search platform that runs your own indexing and querying logic. Instead of adapting your data to someone else’s black box, you bring your Python indexing and querying code and Superlinked provides the compute, orchestration, and observability to run it reliably in your own cloud. At a high level, the process includes:
Use Algolia’s export or browse APIs to extract your full dataset, including all attributes and metadata used for search. These records become the input for your Superlinked indexing code.
Clean, coerce, aggregate, and structure your fields so that each textual, numeric, image, or categorical attribute is clearly defined. This ensures smooth mapping into the schema used by your Superlinked indexing pipeline.
In Superlinked you explicitly define the schema your indexing and querying code will use. Each attribute is mapped to the relevant vector space or structured feature, making it possible to encode titles, descriptions, categories, images, and relational fields with the appropriate embedding models.
During development, your data scientist uses the Superlinked platform to run indexing code directly on their machine for rapid iteration, experimentation, and evaluation. The platform manages access to Superlinked-provided inference services embeddings, re-rankers, and small language models without requiring local GPU setup.
Once ready for production, you deploy the Superlinked platform into your own VPC. The platform runs your indexing and querying code at scale using horizontally scalable CPU workers for execution and GPU-backed inference services for embeddings and re-ranking. It integrates with your existing infrastructure, including your preferred Vector DB, KV store, object storage, and observability tools.
Your data engineering team plugs their pipelines into Superlinked. Depending on your setup, you can push data into the platform (client-initiated push) or let the platform pull from your storage systems (client-initiated pull). Superlinked handles accumulation, joining, hydration, and updating indices in the connected Vector DB to keep your search index continuously synchronized with your primary data stores.
Your software engineers interact with REST APIs exposed by your querying code running inside the Superlinked platform. These APIs execute your logic, hydrate results from the KV store, run semantic scoring, merge multi-round agentic queries, and apply any custom business logic defined by your Python code.
Through the platform’s API, you validate the full flow: ingestion, indexing, semantic scoring, hybrid scoring, and relevance. You can dynamically adjust attribute weighting, iterate on prompt-based query interpretation, or plug in additional embedding or re-ranking models from the Superlinked inference service.
Initially, Superlinked provides the platform along with forward-deployed data scientists who help implement and operate the indexing and querying logic. As the platform matures within your environment, responsibility transitions to your in-house data scientists and eventually to your own infrastructure and operations teams, who manage the deployment entirely in your VPC.
Superlinked remains the platform that orchestrates compute, manages model dependencies, exposes APIs, and provides observability but all code and all data stay under your control.
The following table presents a step-by-step comparison of the key aspects of both search solutions. Understanding these differences will help you choose the right solution for complex, multimodal datasets.
| Feature | Algolia | Superlinked |
| Core architecture | A hosted SaaS search platform that creates optimized indexes using inverted index structures to enable rapid retrieval. | Full stack self-hosted AI search platform that runs your own indexing and querying code with built-in GPU inference, autoscaling, and API orchestration in your VPC. |
| Data modalities | Single-modal search operating primarily on text data and string-based attributes. | Multi-modal search combining text, images, categorical, numeric, and temporal data into unified multi-space embeddings. |
| Relevance model | The ranking algorithm applies customizable rules in sequence like typo tolerance, proximity, attribute relevance, and custom ranking. | Multiple embedding models are combined into a unified vector that captures semantic and structured signals without rule-based ranking. |
| Query-time control | Index relevance is determined at build time through settings like searchableAttributes, customRanking, and synonyms. | Supports weighting at both query definition and run time. This lets you adjust the importance of modal spaces without re-indexing the data. |
| Re-ranking approach | Dynamic re-ranking is a distinct post-retrieval step. It uses AI to identify trends in user behavior and re-ranks search results based on query signals and user interactions. | Performs unified vector search without re-ranking by embedding semantic and structured signals directly into a single vector. Optional re-rankers can be added when needed. |
| Data ingestion | Write operations are asynchronous by design. When you index records through the API, there may be a short delay before the data becomes searchable. | Your indexing code handles ingestion. Data is vectorized through the platform’s inference service and written to your vector DB immediately for real-time search. |
| Deployment model | Fully managed SaaS; self-hosting is not supported. | Self-hosted platform deployed into your cloud or on-prem environment with full control over compute, scaling, and observability. |
Search systems should understand the user's intent and go far beyond simply matching the literal words they type. The true breakthrough in search relevance occurs when all data modalities are connected to naturally reveal deeper meaning.
Superlinked moves beyond keyword-only matching by running your indexing and querying code over unified multimodal embeddings, while enabling dynamic query-time weighting for precise relevance control.
The migration to Superlinked brings search discovery closer to the way people think and interact.
If you want your platform to curate personalized search results for each user, let Superlinked handle the heavy lifting for you. Have questions along the way? Ask your AI Search questions on the Superlinked sub-reddit at r/AskAISearch.
Get started with Superlinked today!
Stay updated with VectorHub
Continue Reading